How to reduce your income tax bill using superannuation
Did you know you can reduce your income tax by making a large personal tax-deductible contribution from your take-home pay to your super? This strategy may be particularly useful if you will be earning more income this financial year or if you have sold an asset this year and made a large capital gain.
What is a personal deductible contribution?
A personal deductible contribution is a type of concessional contribution that you make with your own money and claim as a personal tax deduction in your tax return, subject to meeting certain eligibility criteria (see Are you eligible to make a personal deductible contribution? on page 7).
Other types of concessional contributions include superannuation guarantee (SG) contributions from your employer and amounts you salary sacrifice to superannuation.
The cap on concessional contributions is currently $27,500 per year in 2023/24. However certain individuals may be eligible to use the “catch-up” concessional contribution rules to make a larger contribution.
What are catch-up concessional contributions?
You can carry forward any unused concessional contribution cap amounts that have accrued since 2018/19 for up to five financial years and use them to make concessional contributions in excess of the annual concessional contribution can.
You can make a concessional contribution using the unused carry forward amounts provided your total superannuation balance at the end of the previous financial year (ie, 30 June 2023) is below $500,000.
Once you start to use some of your unused cap amounts, the rules operate on a first-in first-out basis. That is, any unused cap amounts are applied to increase your concessional contribution cap in order from the earliest year to the most recent year. So, when you use some of your unused cap from prior years (by making additional superannuation contributions), the unused cap from the earliest of the five-year period is used first.
And remember, if you don’t use your accrued carry forward amounts after five years, your unused cap amounts will expire. So it’s best to use it before you lose it!
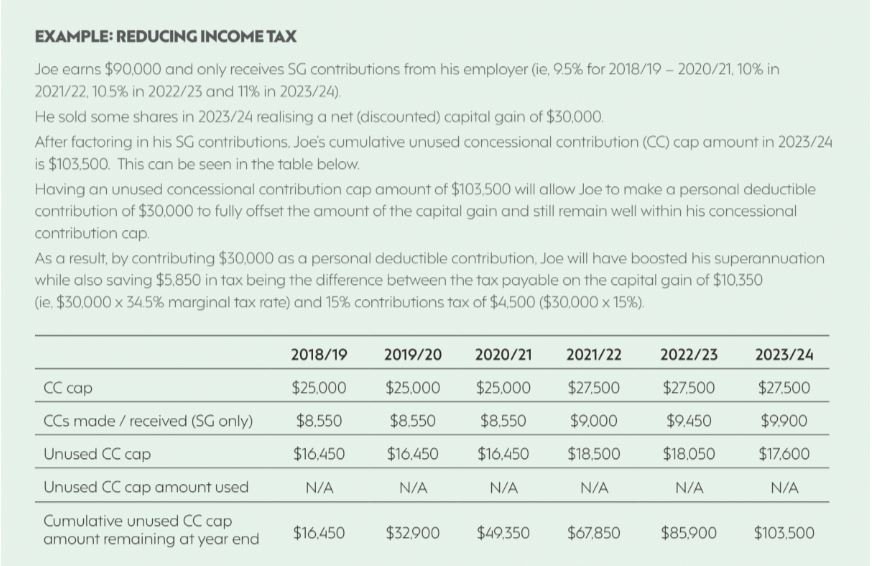
Carry forward contributions may provide strategic opportunities to make larger personal deductible contributions in financial years where you may have a higher level of taxable income, for example, due to assessable capital gains. See the example below.