Who can I nominate as my super beneficiary?
Your superannuation death benefits must be paid to someone when you die. That somebody will usually be your estate or your nominated beneficiary (also known as your dependants).
Paying death benefits to your estate
Unlike other assets such as shares and property, your superannuation and any insurance benefits you have in superannuation do not form part of your estate. That’s because your superannuation is not held by you personally, rather it is held in trust for you by the trustee of your superannuation fund.
However, you can direct your superannuation death benefit to your estate by nominating your ‘legal personal representative’ (LPR), who will usually be the executor of your estate.
If you nominate your estate or LPR, you must also specify in your Will who you want to distribute your superannuation money to. This can include eligible beneficiaries (see below) as well as anyone else you wish to leave your death benefits to.
As such, it’s important that the directions stated in your Will are up to date so your LPR pays out your death benefits (as well as your other estate assets) as per your wishes.
Paying death benefits to a beneficiary/dependant
If you want your superannuation death benefits to be paid to a person, that person must be a ‘dependant’ for super purposes.
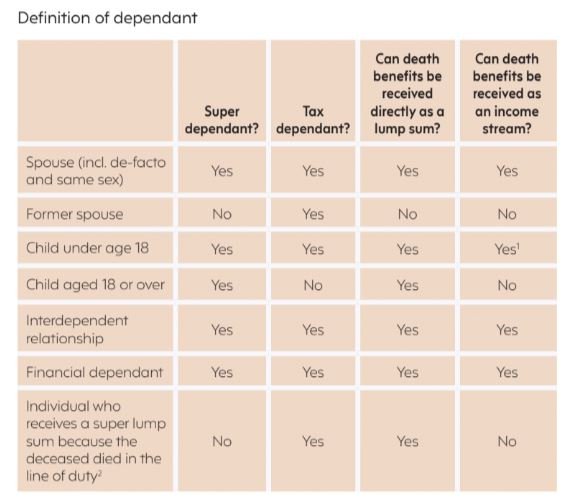
The meaning of dependant is important as it determines who can receive a death benefit, whether the death benefit will be taxed and in what form your death benefit can be paid out (ie, lump sum, income stream, etc).In particular, superannuation law determines who can receive your super directly from your super fund without having to go through your estate. These people are your superannuation dependants. Tax law on the other hand determines who pays tax on your superannuation death benefit. These people are considered tax dependants.
The table below summarises the difference between:
■ a superannuation dependant and tax law dependant, and
■ the types of death benefit that can be paid to each category of dependants.
As can be seen, the key differences between the superannuation and tax dependant definitions are:
■ a tax dependant does not include an adult child (whereas a super dependant does), and
■ a tax dependant includes a former spouse (whereas a super dependant does not).
Although your financially-independent adult children are your superannuation dependants and can receive a death benefit directly from your superannuation fund, they are not tax dependants. This means they will not receive more favourable tax treatment thana tax dependant would receive unless they qualify under an ‘interdependency relationship’ or are financially dependent on you.
A tax dependant will generally not pay any tax on superannuation death benefits. In contrast, a non-tax dependant is taxed on any taxable components of a superannuation death benefit. This could be up to 15% tax plus Medicare levy on any taxable component and potentially up to 30% plus Medicare levy for any taxable untaxed elements within your fund.
Need help?
Please contact us if you would like further information about who you can nominate to receive your superannuation death benefits.